
Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidies (PGT - A) formerly known as preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) is a screening test used to check if genetic or chromosomal abnormalities are present in embryos created through IVF or ICSI before embryo is transferred.
Chromosomal aneuploidies are one of the major causes of infertility and maternal age-related lower pregnancy rate. PGT - A helps to shorten the time to a pregnancy by reducing the need of multiple IVF cycles. Transfer of euploid embryo results in higher pregnancy rates and live birth rates reducing miscarriage risk.
Indications of PGT-A
- Advanced maternal age: 35 years and above.
- Recurrent miscarriages: Women with two or more miscarriages.
- Recurrent IVF failures: Two or more IVF failures
- Severe male factor infertility
Benefits of PGT-A
- Reduced miscarriage rates.
- Higher pregnancy rates per transfer.
- Allows identification and transfer of embryos free of aneuploidy
- Reduces the time to achieve a pregnancy
Procedure
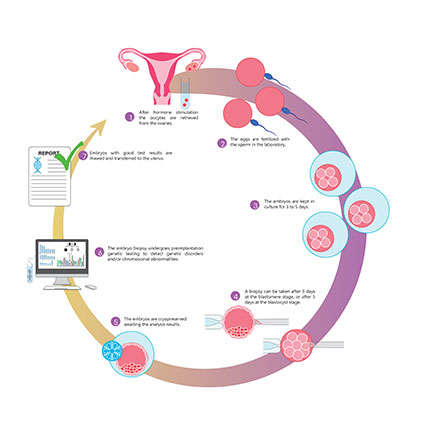
Following the process of egg retrieval and fertilization with the sperm via the ICSI or IVF procedure, the embryos are allowed to grow in the lab for upto 5 days.
A biopsy of a few cells from is taken and sent for genetic testing. Usually it takes few days for the results of the tests to be available, so all the biopsied embryos are frozen.
We will be able to identify the chromosomally normal embryos which will then be transferred into the uterus via a frozen embryo transfer cycle to achieve a healthy pregnancy.
The embryos with chromosomal abnormalities are discarded.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing - M
PGT - M is a procedure, which is used to identify genetic defects within embryos. It is used when one or both the parents have a known genetic disease or disorder that can result in genetic disease in the child or the couple already has an affected child, so that a healthy offspring can be born. This technique can be used to prevent certain genetic diseases or disorders from being passed on to the child.
Some of the couples that can benefit are: Carriers of chromosomal disorders, Sex linked genetic disorders and Single gene disorders.
PGT - M can be done for genetic disorders such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy, neurofibromatosis, sickle cell anemia, Leigh syndrome, retinoblastoma, hereditary inclusion body myopathy, cardiac disorders, and carriers of BRCA1.
We also have several pregnancies in couples carrying mutations for beta thalassemia.